
As the researchers performed KPFS closer and closer to the molecules, they found that the apparent charge distribution in the bonds was distorted by chemical attractions between certain atoms and the cantilever tip.
They studied two molecules that exhibited various charge distributions within chemical bonds, trimeric perfluoro-ortho-phenylene mercury (F 12C 18Hg 3) and its hydrogen-terminated counterpart (H 12C 18Hg 3). Chemistry Stack Exchange without using electronegativity, which one of these molecules is polar closed Ask Question Asked 8 years, 10 months ago Modified 8 years, 10 months ago Viewed 61k times 1 Closed.
Bond polarity how to#
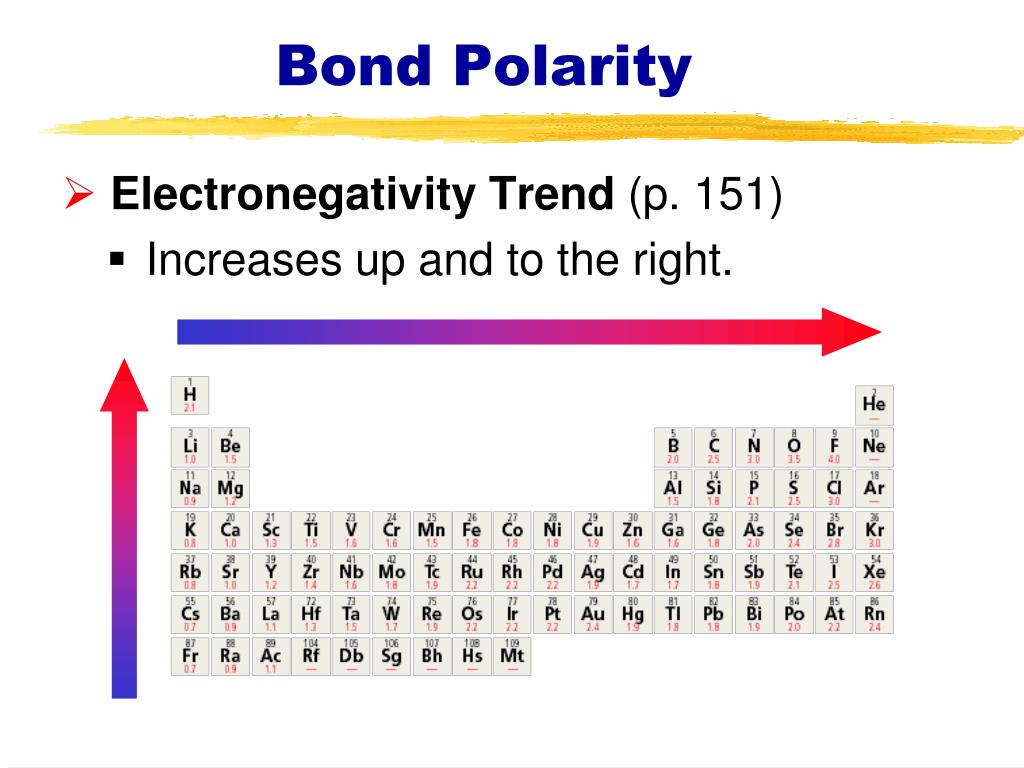
Now Jascha Repp’s group at the University of Regensburg, together with colleagues at the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences, has determined exactly what these influences are, and how to overcome them. explain how polarity of bonds and molecular geometry affects the polarity. Electronegativity is the power of an atom to attract the pair of electrons in a covalent bond towards itself The electron distribution in a covalent bond. Learners are shown how the difference in electronegativity between two bonded nuclei determines the degree of polarity of the bond between them. The shape means most of the negative charge from the oxygen on side of the molecule and the positive charge of the hydrogen atoms is on the other side of the molecule. Polarity of a Water Molecule Water ( H 2 O) is polar because of the bent shape of the molecule. Electronegativity As you can see this means that the electron pair in the covalent bond is (on average) much closer to the fluorine atom compared to the carbon. KPFS might also be precise enough to map the distribution of charges within molecules, but this would require the cantilever tip to be brought very close to a sample where the influence of other chemical forces is uncertain. The polarity of a bondthe extent to which it is polaris determined largely by the relative electronegativities of the bonded atoms. These electrons repel each other, bending the O-H bond away from the linear angle. By varying the voltage, a researcher can measure that surface’s local work function – that is, the strength with which the surface holds on to electrons. By monitoring the resonant frequency of the cantilever, a scientist can determine, with nanometer resolution, the shape and makeup of any surface features.Ī variant of AFM is Kelvin probe force spectroscopy (KPFS), in which the cantilever’s tip applies a bias voltage to a surface. Normal AFM relies on the dynamics of a tiny oscillating cantilever, which is scanned over a surface under study. In a polar molecule, electron density is unevenly distributed throughout the molecule, resulting in regions of.

The new ability could help in the design of solar cells, by unmasking the generation of charge carriers and how they hop to and from electrodes. polarity, in chemical bonding, the distribution of electrical charge over the atoms joined by the bond. Polar Bonds polar bond: a covalent bond that has opposite partial charges on each side (one side partially positive and one side partially negative), because. (Credit: Jodi So Source: CK-12 Foundation License: CC BY-NC 3.Researchers in Germany and the Czech Republic have improved the clarity of atomic force microscopy (AFM) to probe the distribution of charges within atoms and molecules. This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into bond polarity, electronegativity, and the dipole moment of a bond. \): A nonpolar covalent bond is one in which the distribution of electron density between the two atoms is equal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
